Table of Contents
What is a Retaining Wall?
A retaining wall is like a strong wall that holds back, or “retains,” the soil behind it. It helps to prevent the soil from sliding or eroding, especially on hills or sloped areas. Think of it as a superhero wall that keeps the land in place and makes sure everything stays nice and sturdy. We’ll also talk about the types of retaining wall
Functions of Retaining Wall
Retaining walls serve various functions to provide stability and support to the land. Here are different functions of retaining walls:
1. Erosion Control:
- Retaining walls help prevent soil erosion by holding back and stabilizing the earth on slopes.
2. Support on Slopes:
- They offer structural support to prevent the collapse of soil on steep slopes or hilly areas.
3. Terracing:
- Retaining walls can create terraced levels on a slope, making it easier to plant gardens or create flat areas for various uses.
5. Land Utilization:
- By creating flat surfaces on slopes, retaining walls allow for better utilization of land, making it suitable for construction, landscaping, or other purposes.
6. Property Enhancement:
- Retaining walls enhance the aesthetic appeal of properties by creating visually pleasing landscapes, especially in hilly or uneven terrains.
7. Prevention of Sinkholes:
- In areas with potential sinkhole formation, retaining walls can stabilize the soil and prevent the occurrence of sinkholes.
8. Structural Support for Roads:
- Retaining walls provide support to roads built on slopes, preventing soil movement and ensuring the stability of the road infrastructure.
9. Protection Against Landslides:
- In areas prone to landslides, retaining walls act as barriers to minimize the risk and protect structures and landscapes.
Types of Retaining Wall
Retaining walls come in various types, each designed to address specific needs and conditions. Here are common types of retaining walls:
1. Gravity Retaining Walls:
- These walls rely on their weight and mass to resist the pressure of the soil behind them. They are typically thick at the base and taper towards the top.

2. Cantilever Retaining Walls:
- Cantilever walls have a horizontal base that extends backward into the retained soil. They use the principles of leverage to resist the pressure from the soil.
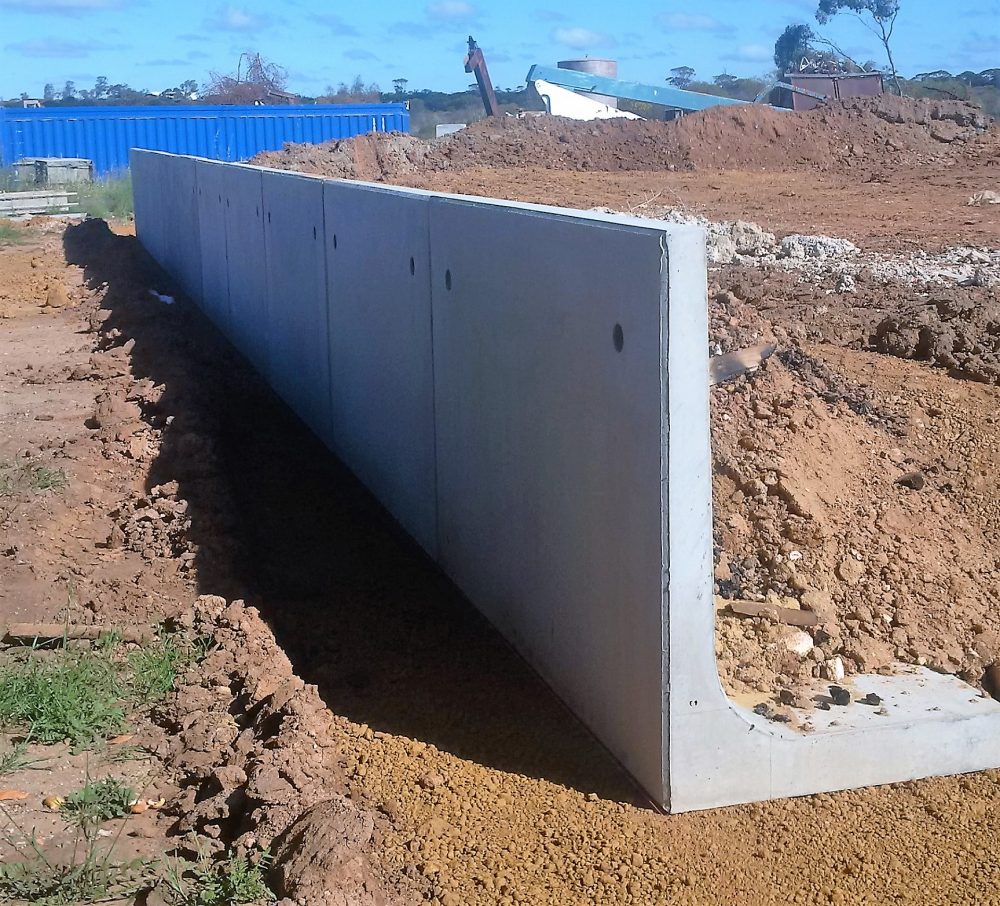

3. Counterfort Retaining Walls:
- Similar to cantilever walls, counterfort walls have additional vertical columns, called counterforts, on the earth side. This enhances the wall’s stability.
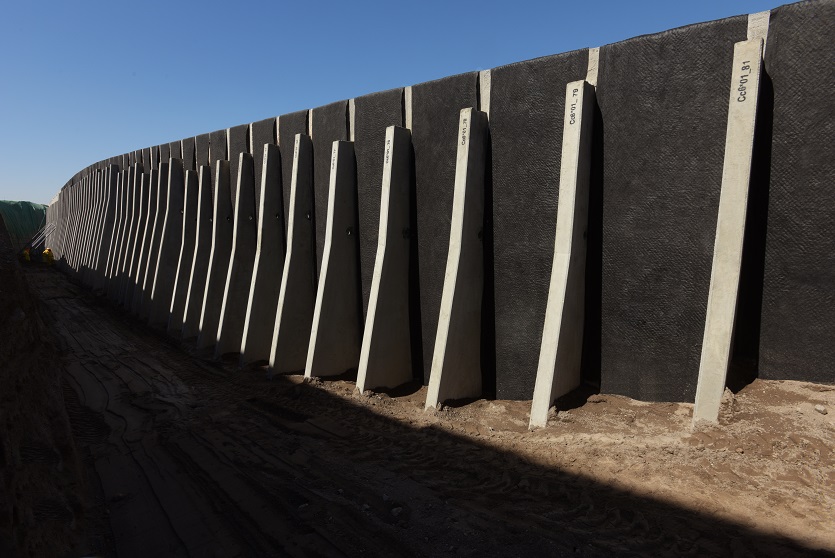

4. Anchored Retaining Walls:
- Anchored walls use cables or stays anchored in the soil or rock behind the wall. This type is suitable for tall or challenging conditions.
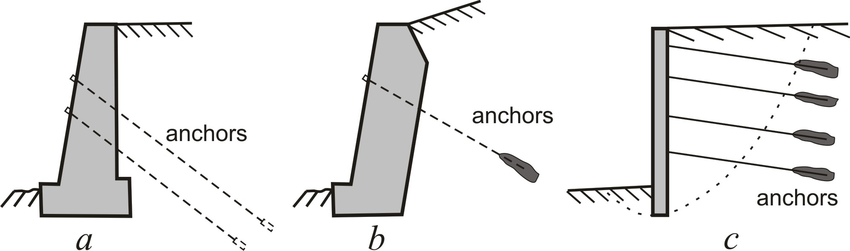
5. Sheet Pile Retaining Walls:
- Sheet pile walls are made of interlocking steel, vinyl, or wood sheets driven into the ground. They are effective in areas with soft or loose soils.

6. Crib Retaining Walls:
- Crib walls are constructed by stacking interlocking concrete or timber boxes. They provide a sturdy structure for retaining soil.
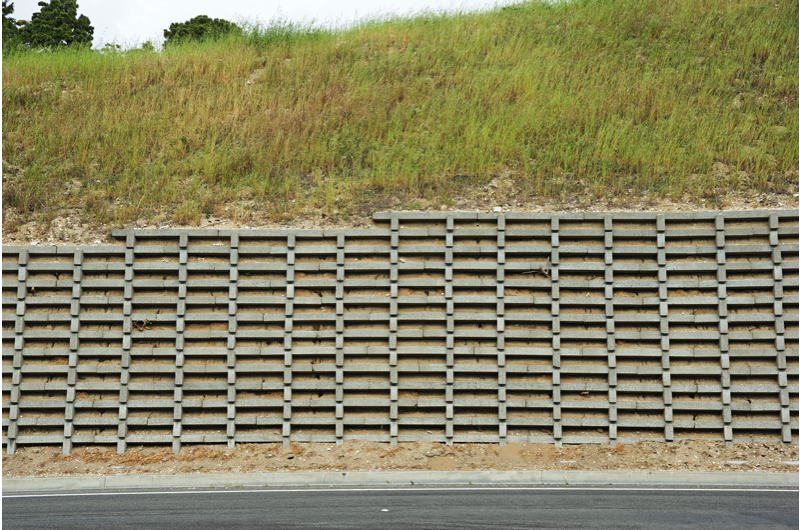

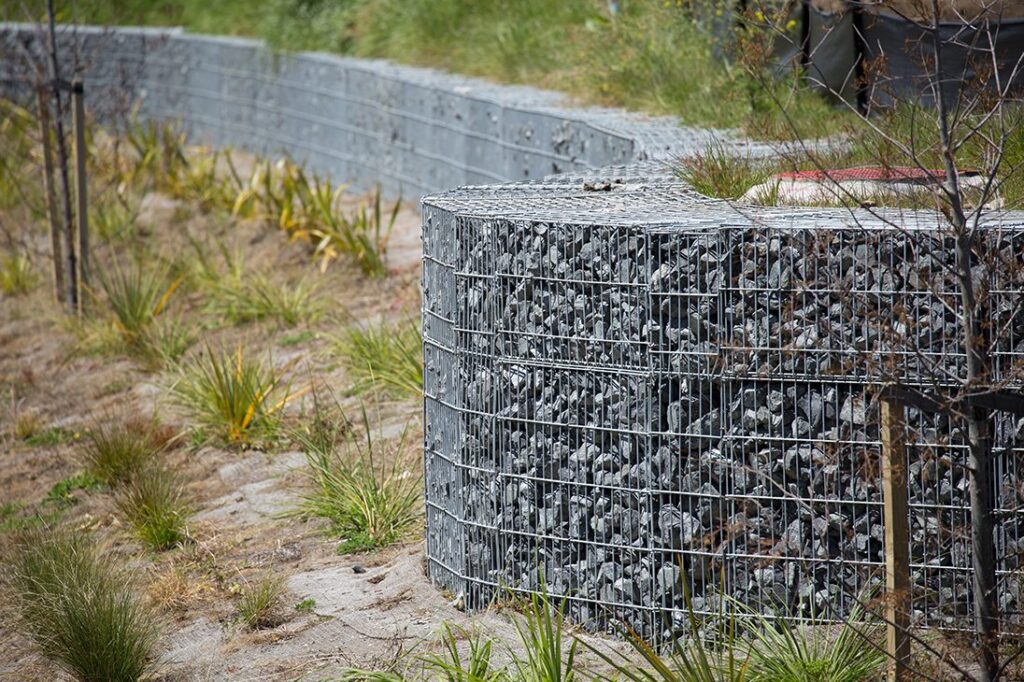
7. Gabion Retaining Walls:
- Gabion walls use wire baskets filled with stones or other materials. They are flexible, allowing water drainage, and can adapt to the movement of the soil.

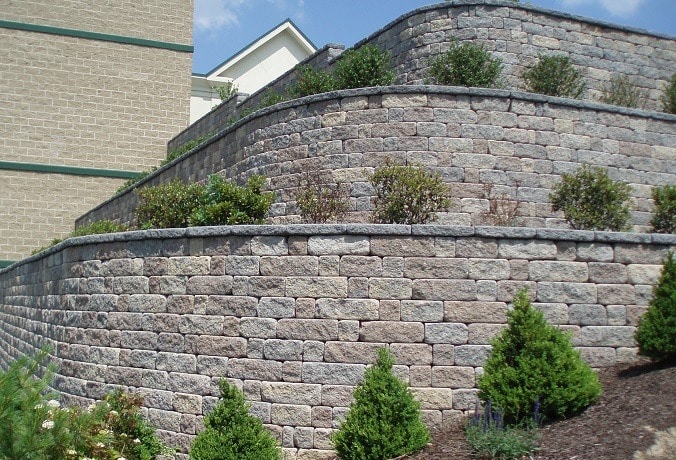
8. Segmental Retaining Walls:
- These walls consist of individual precast concrete blocks or units that fit together like puzzle pieces. They are commonly used for landscaping.

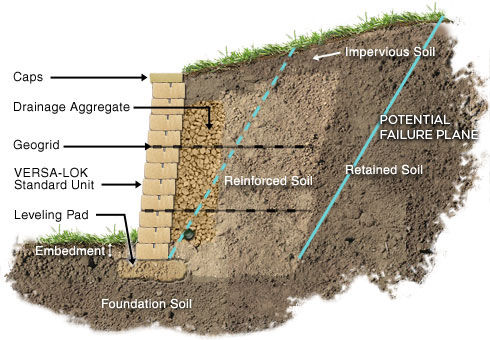
9. Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls:
- Reinforced soil walls use layers of geogrid reinforcements to stabilize the soil. They are a cost-effective option for various applications.
10. Tied Back Retaining Walls:
– Tied back walls use horizontal supports (anchors or cables) extending into the retained soil. They are effective for resisting lateral soil pressure.
Conclusion
Choosing the appropriate type of retaining wall depends on factors such as the height of the wall, soil conditions, drainage requirements, and aesthetic preferences.
We hope you find this content useful. Please kindly take time to follow us on on facebook, and instagram.



